Integrated pest management effectively rids your home or yard of pest problems while remaining mindful of your environment. It considers the whole ecosystem and uses common-sense practices that target pest life cycles and how they interact with their environment.
Integrated pest management is more than treating an area with harsh chemicals and hoping the pests react. It relies on strategic, comprehensive solutions that are highly effective and economical, and it aims to be gentler on humans, other animals, and surrounding property. Methods may vary from pest to pest and may require the use of chemicals depending on the target, but on the whole, integrated pest control is designed around a holistic approach to pest control.
Where Can I Use Integrated Pest Management?
Integrated pest management can be applied to agricultural settings, including:
- Crop fields
- Forests
- Gardens
- Grazing fields
- Lawns
It is also effective for non-agricultural applications, such as:
- Homes
- Commercial buildings
- Public properties
Anywhere a pest can thrive, integrated pest management can treat the area and manage the pest presence over time.
What Pests Are Treated with Integrated Pest Management?
All pest types can be treated with the right integrated pest management methods (even non-insects, like weeds and rodents).
The pests that Bizzy Bee Exterminators effectively treat include:
- Ants (including fire ants)
- Bed bugs
- Centipedes
- Cockroaches
- Crickets
- Lady bugs
- Mice
- Millipedes
- Mosquitos
- Scorpions
- Spiders
- Stink bugs
- Termites
What Are the Steps to Integrated Pest Management?
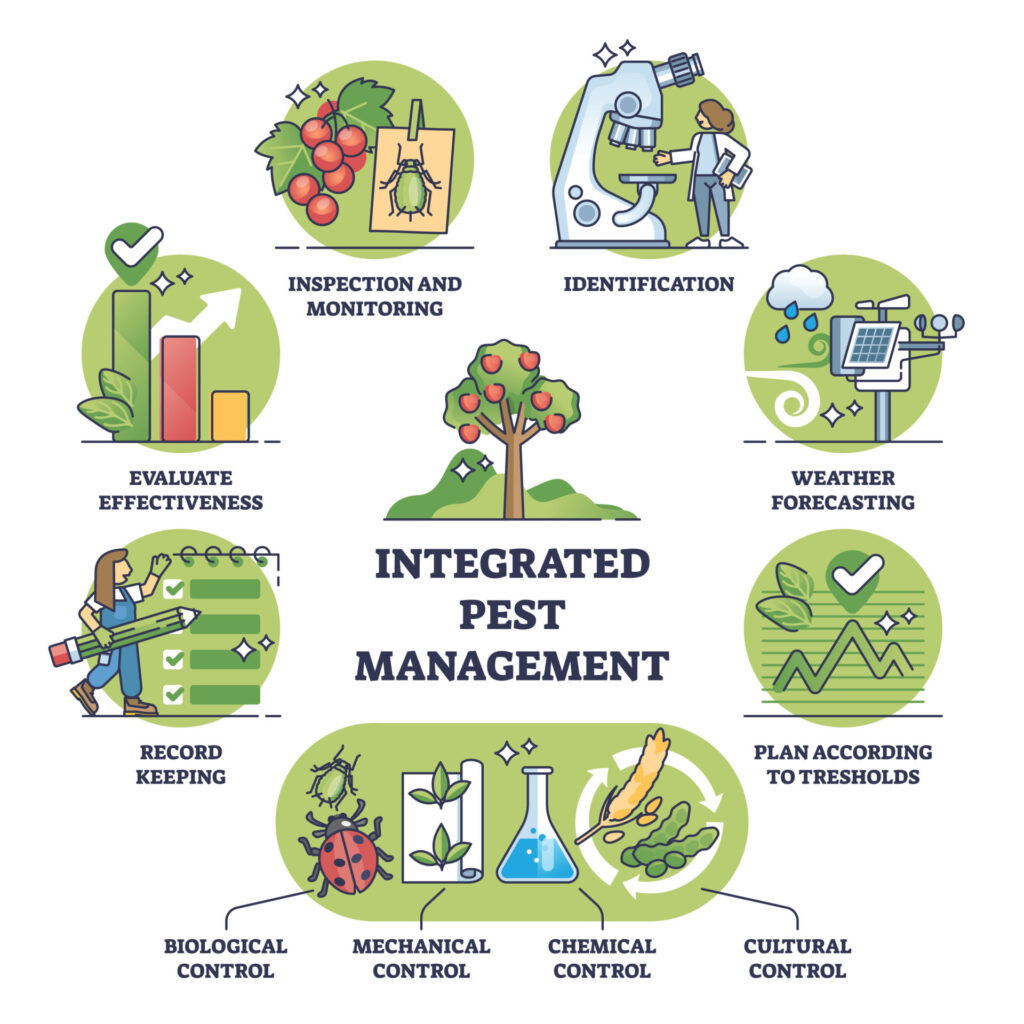
The steps to integrated pest management will vary from pest to pest, but overall, the general steps include:
Analyzing the Infestation or Treatment Area
Before any action is taken, a professional exterminator should evaluate where treatment is needed or wanted. It is critical to determine if there is a pest problem in a specific area or if the presence of a certain pest is minimal.
The exterminator also needs to know the area’s environmental factors and the pest’s relationship to those factors. If a home is infested with roaches, what are the factors within the home that provide such desirable living conditions for roaches? If a yard is infested with mosquitoes, what does the yard feature that has drawn so many mosquitoes to it? An analysis is crucial to understanding which treatment to apply and which actions to take to stop an infestation and prevent one from occurring again.
Additionally, in most cases, sighting an insect or two is not a cause for concern or a sign that you need pest management. An analysis can provide deeper insight into the area and show the degree to which integrated pest management is required.
Identify & Monitor
Within the analysis, your exterminator should identify the pests present and monitor any damage they may have caused to determine whether one-time treatment, ongoing treatment, or no treatment is needed to manage the area. Homeowners or landowners can spot a certain type of pest but not realize others in the area need to be controlled, too. Or, it’s possible to spot a pest and assume control is needed when it is not.
Applying Treatment and Pest Management
There are several ways to treat pests and manage the area so they do not reinfest. Integrated pest management utilizes a combination of approaches and methods, which include:
Biological Pest Control
Biological control for pest management uses other organisms – a pest’s natural enemies, predators, and competitors – to reduce the pest population and prevent it from returning. These organisms can include other insects, animals, pathogens, and parasites. Biological control is most appropriate and effective for outdoor areas.
Examples of biological control include:
- Installing bat boxes in your yard since bats are a predator for mosquitoes.
- Planting mint to repel wasps and yellowjackets.
- Introducing predatory insects to your garden to eliminate plant-destroying aphids, mites, and scale insects.
Chemical Pest Control

Chemical pest control means applying pesticides. Ideally, pesticide is used on an as-needed basis and is not the only go-to for treatment and control. It is also ideal to choose the best environmental options and minimize the harm caused to humans, animals, and nontargeted insects or plants. Pesticide applications, when carried out appropriately, can be extremely effective at eliminating pests and keeping them away for good.
Examples of chemical control include:
- Installing termite baiting stations around your yard.
- Spot-spraying mosquito nests or areas in the yard that are likely to attract mosquitoes.
- Applying contact chemicals to a home’s doorways, window panes, and other entry areas.
Cultural Pest Control
Cultural control means manipulating an area to target pests and discourage them from infesting or damaging an area. It can also mean strategically using surrounding factors to your advantage to avoid anything from overtaking an area. Cultural control is all about manipulating environmental factors to negatively impact a pest and minimize its ability to establish itself in one area, reproduce, and survive. Like biological control, cultural pest control is best for outdoor areas. Cultural control is also often combined with biological control methods for effective management.
Examples of cultural control include:
- Rotating crops or garden plants to different sites or waiting between several harvests to replant a certain crop in the same area.
- Planting “trap crops” that attract pests to keep the protected plant or crop pest-free.
- Planting crops or plants at a certain time in the season to reduce the likelihood of a pest reaching it and damaging it.
Mechanical Pest Control
Mechanical pest control is a non-chemical form of management designed to target a pest and kill it, block it from a specific area, or destroy its environment. Mechanical control, sometimes called physical control, can effectively eliminate pests, especially in combination with other forms of integrated pest management.
Examples of mechanical control include:
- Installing mouse traps around your home.
- Installing bug-stopping screens around your porch.
- Installing electric traps (bug zappers) around your house or targeted area.
For exceptional pest control that considers all angles of integrated pest management, turn to the experts at Bizzy Bee Exterminators.
Let our team help you eliminate pests and keep them away from your home or property for good.
Call us to schedule pest control and pest management at your home today: 1-800-273-4958
Recent Articles
